An initiative towards greener environment
Subhadeep Chakraborty1 , Dr. Abhijit Bandyopadhyay1*
Subhadeep Chakraborty, Dr. Abhijit Bandyopadhyay*
Department of Polymer Science and Technology, University of Calcutta, 92, A.P.C. Road, Calcutta 700009, India
*Corresponding author: Subhadeep Chakraborty, Department of Polymer Science and Technology, University of Calcutta, 92, A.P.C. Road, Calcutta 700009, India. Tel: 8617435667; E-mail: schakraborty.764@gmail.com
Received date: June 20, 2020; Accepted date: August 20, 2021; Published date: August 29, 2021
Citation:Subhadeep Chakraborty (2021) Treatment of waste water by new age architectural polymers -an initiative towards greener environment. . J Org Inorg Chem.Vol.7 No.4.
Abstract
The world is making progress day by day and making our life easier. The most important role in this regard is played by the industries. Thus, the development of the society and hence the mankind is totally depends on industrialization. Industries play a dual role one is directly and another indirectly. The first one is that, industries make the thing which we needed daily and on the other hand it causes pollution. Air pollution, sound pollution, water pollution, soil pollution are some of the main pollutions occurs due to the adverse effect of industries. The source of different kind of pollution varies from one another. But, the main source of water pollution is the discharge of industrial effluents. Last few decades have witnessed the discharge of huge amount of industrial waste water in to the nearby fresh water bodies. Therefore, it pollutes the source of fresh water. It results into severe pollution causing adverse effect on the human and the ecosystem. The worst sufferers are the aquatic lives. Thus the industrial waste water are needed to be treated before its discharge to the environment(Rajaram & Das, 2008)
Introduction
The world is making progress day by day and making our life easier. The most important role in this regard is played by the industries. Thus, the development of the society and hence the mankind is totally depends on industrialization. Industries play a dual role one is directly and another indirectly. The first one is that, industries make the thing which we needed daily and on the other hand it causes pollution. Air pollution, sound pollution, water pollution, soil pollution are some of the main pollutions occurs due to the adverse effect of industries. The source of different kind of pollution varies from one another. But, the main source of water pollution is the discharge of industrial effluents. Last few decades have witnessed the discharge of huge amount of industrial waste water in to the nearby fresh water bodies. Therefore, it pollutes the source of fresh water. It results into severe pollution causing adverse effect on the human and the ecosystem. The worst sufferers are the aquatic lives. Thus the industrial waste water are needed to be treated before its discharge to the environment(Rajaram & Das, 2008).
Different kind of industries produces different kind of waste water. The combination of the pollutant varies from sector to sector. It depends on the type of effluent produced from the industries. There are two types of effluent(Industrial Waste — Safe Drinking Water Foundation, n.d.)
- Organic
- Inorganic
The different type of effluents needs different treatment.
Iron and steel industries produces mainly metal ions, some acids, and phenolic compounds etc. as effluents(Patterson, 1985). The textile industries produce compounds of sulphates and chromium as industrial effluents. Same kind of pollutants comes out from leather industries.
Ceramic and cosmetics industries produce kaolin as industrial effluent(Gu et al., 2015). Chemical industries produces hazardous chemical and toxic metal ion as an effluent. Petrochemical industries produce mineral oils as an effluent(Shrivastava & R.L., 2017). Mining industries produces metals, acid etc. as an effluent(Review of Water Pollution Problems and Control Strategies in the South African Mining Industry | Water Science and Technology | IWA Publishing, n.d.). Here is the list of all the pollutants produced from different kind of industries.
| Industries | Effluents |
|---|---|
| Iron and steel | Mainly metal ions, some acids, phenolic compounds etc. |
| Textiles | Compounds of sulfates and chromium |
| Paper | Organic compounds containing chlorine |
| Ceramic and cosmetics | Kaolin |
| Chemicals | Hazardous chemicals, toxic metal ions |
| Petrochemicals | Mineral oils |
| Mining | Metals, acids etc. |
The settling and filtration and hence separation of these effluent becomes difficult mainly due to the small size of the particles and presence of surface charge over these particles. So, it becomes very challenging to the research world for the treatment of these industrial effluents. There are various methods available for the treatment of the waste water. These are listed as below:
- Ion exchange
- Membrane filtration
- Precipitation
- Flotation
- Solvent extraction
- Adsorption
- Coagulation
- Flocculation
- Biological and electrolytic
Flocculation
Flocculation is the process of forming agglomeration of small suspended particles into large sized flocs and settling down due to the force of gravity. The process of flocculation is simple, effective, requires less time and can be extensively used for various types of waste water(Singh et al., 2003).
Coagulation
Coagulation is the process of destabilization of colloids via addition of chemical and this occurs by neutralization of charges. Commonly used coagulants are alum, polyaluminum chloride (PAC), ferric chloride, ferrous sulphate, calcium chloride, magnesium chloride. But the application of coagulants is limited due to the following reasons:
- Higher dosage requirement
- Production of large amount of toxic sludge
- Disposal problem
- Causing numerous health hazards (PAC causes Alzheimer’s)
- Sensitivity to pH
- Inefficient in cold condition
- Not good for fine particles
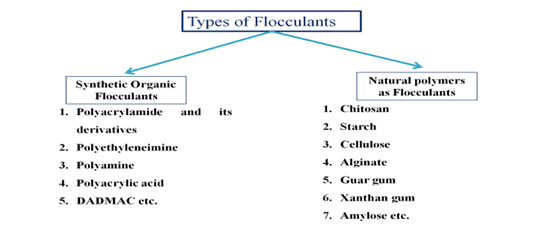
Flocculants are of two types
- Synthetic organic flocculants
- Natural polymers as flocculants
But there are some pros and cons of using synthetic polymers as flocculating agent:
Pros
- Tailor made
- Controlled molecular weight
- Controlled molecular weight distribution
- Desirable functional groups
- Can be modified
- Efficient flocculation
Cons
- Non-biodegradable
- Shear resistant
- Unreacted monomers have toxic effects
Not only these synthetic polymers but also the natural polymers have some pros and cons which are listed as below:
Pros
- Low molecular weight
- Shear stable
- Bio-degradable
- Cheap
- Easily available
- Non-toxic
Cons
- Biodegradability reduces shelf life
- Requires larger dosage
- Flocs are unstable in nature
To overcome these difficulties natural polysaccharides are grafted with synthetic monomers on the polymeric backbone. The advantages of grafting can be listed below:
Advantages
- Decrease in bio-degradable nature
- Increase in percentage of synthetic monomers
- Due to grafting shear stability increases
- Also due to the presence of polysaccharide backbone it is also biodegradable
- Approachability of polymeric chains towards contaminants increases
It has been found that the graft copolymers having fewer and longer chains are more effective flocculants(Bazoubandi & Soares, 2020).
Mode of synthesis of graft copolymers
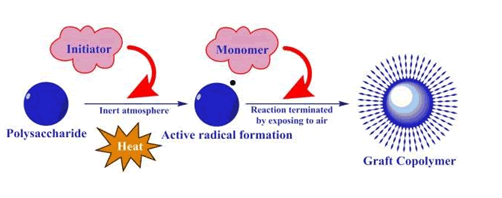
Chemical method
In this method the natural polysaccharides are at first dissolved in distilled water and the monomer is added. After homogenization, inert atmosphere is created by using nitrogen gas and then initiator is added. The reaction is allowed to do for 4 hours and after completion of reaction, it will be terminated by restriction of nitrogen gas and exposing to the atmospheric oxygen.
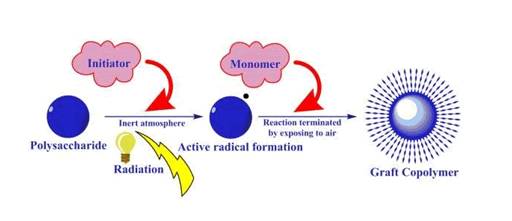
Radiation induced grafting
In this method the natural polysaccharides are at first irradiated with source of ionizing radiation and the monomer is added. After homogenization, inert atmosphere is created by using nitrogen gas and then initiator is added. The reaction is allowed to do for few minutes and after completion of reaction, it will be terminated by restriction of nitrogen gas and exposing to the atmospheric oxygen(Singh et al., 2003).
Materials required
The materials that are essential for the synthesis of graft copolymer by chemical method can be listed as follows:
- Polysaccharide (chitosan, xanthan gum, starch )
- Vinyl monomers ( acryl amide, acrylic acids etc)
- Initiator (KPS, APS)
- Distilled water
- Acetone
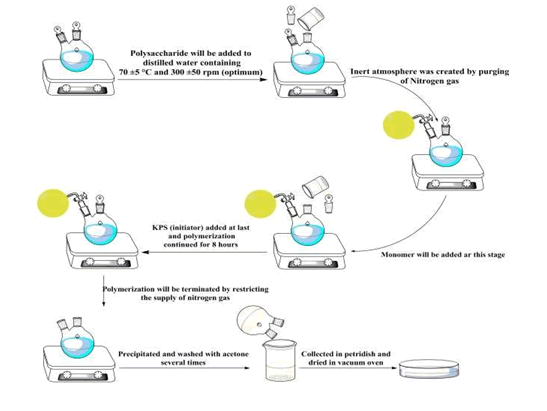
Scheme of synthesis
The polysaccharide will be dispersed in distilled water at some heating temperature and under continuous stirring. Inert atmosphere created by the continuous purging of nitrogen gas to the system. monomer solution to be added to the polymer solution and keep on stirring to become homogenous. Then, solution of initiator is added to the system and added to polymerize for several hours. After completing the polymerization, the reaction will be terminated by exposure to the atmosphere and restricting the supply of nitrogen gas. The graft copolymer is then precipitated in acetone and dried to constant weight(Molatlhegi & Alagha, 2017).
Reaction
The active radical formation takes place on the surface of the polymeric backbone. The radical then attack on the double bond of the vinyl monomer and the grafting goes on. The polymerization then continues and the reaction is terminated by exposure to oxygen(Kolya et al., 2017).
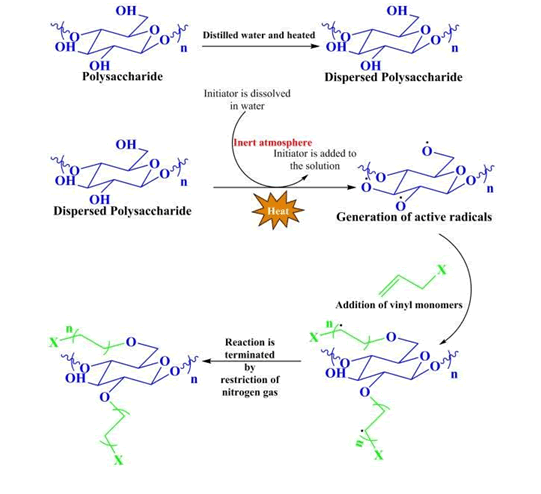
Degree of grafting
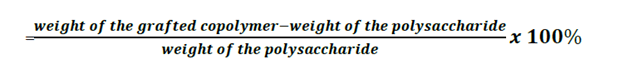
Mechanism of flocculation
Flocculation occurs mainly by two mechanisms (Lee et al., 2014):
- Charge neutralization: This type of mechanism is prevalent when the graft copolymer carries positive charges and the effluent is negatively charged. The agglomeration formation occurs due to the neutralization of charges over both of Them.
- Bridging mechanism: This type of mechanism is prevalent when the long chain polymers having high molecular weight and low charge density adsorbed over the surfaces of particles such that loops and tails that extend far beyond the electrical double layer.
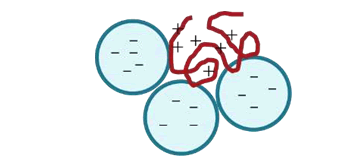
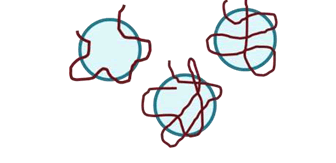
Characterization
After graft copolymer formation, it will be thoroughly washed with solution to remove unreacted monomers, polymers and any other impurities. It is then characterized by several analytical techniques to identify the structural properties. The techniques are listed below (Kolya et al., 2017):
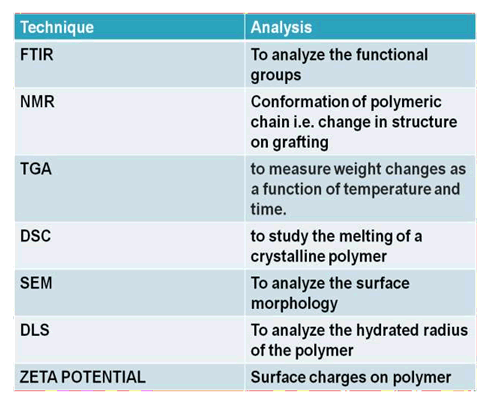
Examples of graft copolymers
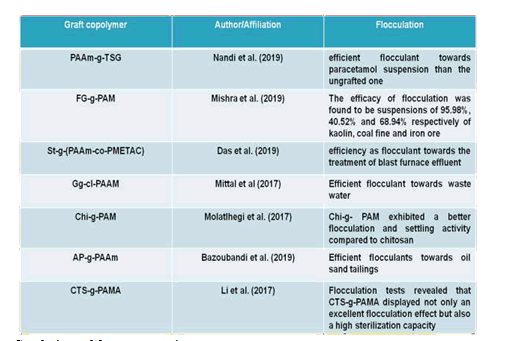
The examples of graft copolymers has been listed (Bazoubandi & Soares, 2020; Das et al., 2019; Li et al., 2017; Mishra & Kundu, 2019; Mittal et al., 2018; Molatlhegi & Alagha, 2017, 2017; Nandi et al., 2019)below(Bazoubandi & Soares, 2020; Molatlhegi & Alagha, 2017; Li et al., 2017; Nandi et al., 2019; Das et al., 2019; Mittal et al., 2018; Mishra & Kundu, 2019)
Conclusion and future perspective
- The application of conventional flocculant has been well tested and verified on waste water
- Shows remarkable results in removal of TSS, turbidity, COD, color removal sometimes upto 90%
- Future works on producing best flocculant that can work in wide range of pH
- Research should be carried out to see how molecular weight and charge distribution affects flocculation
- Optimization should be done to get effective flocculation at lower cost
- Industrial research work should be carried out for its real time application
References
- Bazoubandi B., & Soares J. B. P. (2020). Amylopectin-graft-polyacrylamide for the flocculation and dewatering of oil sands tailings. Minerals Engineering, 148: 106196.
- Das S., Patra P., Singha K., Biswas P., Sarkar S., & Pal S. (2019). Graft copolymeric flocculant using functionalized starch towards treatment of blast furnace effluent. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 125: 35â??40.
- Gu Y., Xu, J Keller, A. A. Yuan D., Li Y., Zhang B., Weng Q., Zhang X., Deng , Wang H., & Li F. (2015). Calculation of water footprint of the iron and steel industry: a case study in Eastern China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 92: 274â??281.
- Industrial Waste â?? Safe Drinking Water Foundation. (n.d.).
- Kolya H., Sasmal D., & Tripathy T. (2017). Novel Biodegradable Flocculating Agents Based on Grafted Starch Family for the Industrial Effluent Treatment. Journal of Polymers and the Environment, 25: 408â??418.
- Lee C. S., Robinson J., & Chong M. F. (2014). A review on application of flocculants in wastewater treatment. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 92: 489â??508.
- Li X., Zheng H., Wang Y., Sun Y., Xu B., & Zhao C. (2017). Fabricating an enhanced sterilization chitosan-based flocculants: Synthesis, characterization, evaluation of sterilization and flocculation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 319: 119â??130.
- Mishra S., & Kundu K. (2019). Synthesis, characterization and applications of polyacrylamide grafted fenugreek gum (FG-g-PAM) as flocculant: Microwave vs thermal synthesis approach. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 141: 792â??808.
- Mittal H., Kumar V., Alhassan S. M., & Ray S. S. (2018). Modification of gum ghatti via grafting with acrylamide and analysis of its flocculation, adsorption, and biodegradation properties. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 114: 283â??294.
- Molatlhegi O., & Alagha L. (2017). Adsorption characteristics of chitosan grafted copolymer on kaolin. Applied Clay Science, 150: 342â??353.
- Nandi G., Changder A., & Ghosh L. K. (2019). Graft-copolymer of polyacrylamide-tamarind seed gum: Synthesis, characterization and evaluation of flocculating potential in peroral paracetamol suspension. Carbohydrate Polymers, 215: 213â??225.
- Patterson J. W. (1985). Industrial wastewater treatment technology, Second edition.
- Rajaram, T., & Das, A. (2008). Water pollution by industrial effluents in India: Discharge scenarios and case for participatory ecosystem specific local regulation. Futures, 40: 56â??69.
- Review of Water Pollution Problems and Control Strategies in the South African Mining Industry | Water Science and Technology | IWA Publishing. (n.d.).
- Shrivastava S., & R.L., S. (2017). A systematic literature review on green manufacturing concepts in cement industries. International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management, 34: 68â??90.
- Singh R. P., Nayak B. R., Biswal D. R., Tripathy T., & Banik K. (2003). Biobased polymeric flocculants for industrial effluent treatment. Materials Research Innovations, 7: 331â?? 340.
Open Access Journals
- Aquaculture & Veterinary Science
- Chemistry & Chemical Sciences
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Health Care & Nursing
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Materials Science
- Mathematics & Physics
- Medical Sciences
- Neurology & Psychiatry
- Oncology & Cancer Science
- Pharmaceutical Sciences
