Car wash Shampoo Formulations.
Hebah Abdel-Wahab1* and Tamara Gund 2
1Department of Chemistry, Hudson County Community College, Jersey City, USA
2Department of Chemistry and Environmental Science, New Jersey Institute of Technology, New York, USA
- *Corresponding Author:
- Hebah Abdel-Wahab
Department of Chemistry,
Hudson County Community College, Jersey City,
USA,
E-mail: dr.heathera@gmail.com
Received date: August 12, 2022, Manuscript No. IPJOIC-22-14169; Editor Assigned date: August 15, 2022, PreQC No. IPJOIC-22-14169 (PQ); Reviewed date: August 26, 2022, QC No. IPJOIC-22-14169; Revised date: September 06, 2022, Manuscript No. IPJOIC-22-14169 (R); Published date: September 14, 2022, DOI: 10.36648/2472-1123.8.5.22
Citation: Wahab HA, Gund T (2022) Car wash Shampoo Formulations. J Org Inorg Chem Vol.8 No.5:22
Abstract
The market for vehicle cleaning products in Western Europe has approached a value of $400 million dollars in 2007. Domestic and industrial automated cleaning of vehicles can include four main steps, pre-wash, main wash, rinse and drying besides the manual cleaning of domestic vehicles. The objective of this work is to find chemical compounds and additives that would increase the quality of the car wash shampoo concentrate, exclude chemical compounds that would decrease the quality of the current formulation and make 1 L of concentrate dilute to 500 L for its use and distribution. It has been found that the amount of surfactants used in the current formulation is low compared to the amounts used in references, the solvents used in the current formulation are humectants and are only used in personal care products not in car wash shampoos, and some chemical compounds that would make high quality car wash shampoos are missing from the current formulation lowering its quality: Emulsifying/foaming agents (3%), some builders (5%), and solvents that would dissolve grease are missing from the current formulation (4%). For a Liter of concentrate dilute to 500 L, the amount of builders, solvents and surfactants must be increased to 1½ and the amount of water must be decreased to ½.
Introduction
An international company in on Canada is looking to improve chemical properties of their carwash shampoo. A liter of carwash shampoo concentrate dilutes only to 200 L using the current formulation. The formulation consists of the following chemical compounds: 5% Linear Alkyl Benzene Sulphonic Acid (LABSA), 20% Sodium Lauryl Ether Sulphate (SLES), 5% Sodium Lauryl Sulphate (SLS), 1% Sodium hydroxide, 2% Betaine, 61.5% Water, 3% Sodium triphosphate, 2% Glycerol, and 0.5% Propylene glycol [1].
Car maintenance products are classified into interior and exterior car care products. Interior car care products are deodorants, grease cleaners, vinyl and plastic cleaners and polishes, interior wins screen cleaners, carpet shampoos and leather polishes. Interior car care products include tire dressings dressings and cleaners, pre-soak detergents, car polishes, wash and wax formulations, windscreen cleaners, water repellents and drying aids and wheel rim cleaners. The climate and the season of the year affect the nature of the soiling of the vehicle and the ease of its removal [2].
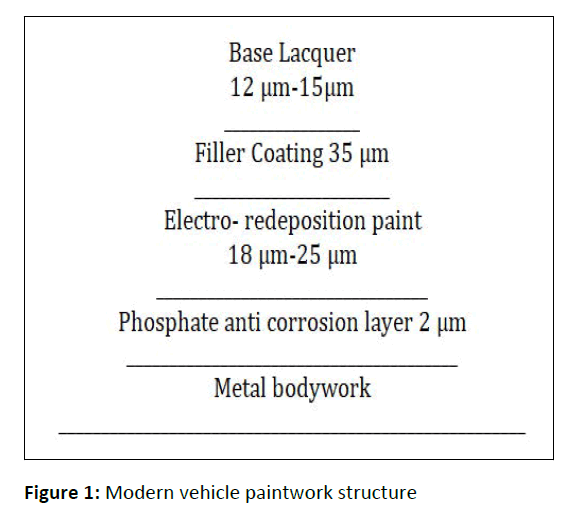
The bodywork of the automobile is of consist of multiple coatings; each coating provides a variety of functions. Figure 1 shows the coating layers in the bodywork of modern cars. The paintwork of the vehicle is the external surface to be cleaned.
The base coat is usually water based polymeric binders, fillers and pigments. The inner coating, the electro-deposition paint and the phosphate based anti-corrosion layer provide protection to the metal surface. On top of the protective coatings is the filler layer, it must have an excellent adhesion property to both top-coat and the base coat. The finishing lacquer must have good impact strength, retain gloss and it must be waterproof. Domestic and industrial automated cleaning of vehicles can be divided into four main steps, pre-wash, main wash, rinse and drying besides the manual cleaning of domestic vehicles. Prewash includes cold degreaser, micro emulsion and foam washes. Main wash includes shampoo and micro emulsion. Rinse includes hot/cold wax and rinse aid [3].
Car shampoos can be either in liquid or in powder form. Liquid car shampoos are a combination of binders, surfactants and liquids dissolved in water as the main solvent. These products are easily too rinsed off, high foaming, biodegradable, made to cut through grease on the bodywork and they don’t damage any part of vehicle surface including the paintwork. Economy car shampoos do not contain builders. Powder car shampoos are made of a mixture of builders (carbonates, phosphates or metasilicates) and surfactants (fatty alcohol ethoxylates or dodecylbenzene sulphonates) absorbed onto the powder. The main anionic detergent can be either alkylbenzene sulphonates and/or sodium lauryl ether sulfates. Sodium lauryl ether sulfates is incorporated into the formulation used when denser richer foam is required. Fatty acid alkanolamides, amine oxide or betaine is used in the formulation for viscosity and to stabilize the foam produced. For greater foam stability and viscosity, amides are added to the formulation. To increase the quantity of the foam produced, betaines and amine oxides are used. Glycerol ether is used to ease grease removal. Secondary surfactants are used for viscosity and foam modifications, and are also used to enhance spot removal and to improve detergency. Binders such as phosphates (0.5%-2.5%) are added to improve detergency (Table 1).
| Chemical compound | % By weight used the formulation |
|---|---|
| Sodium carbonate (binders) | 2% |
| Sodium metasilicate pentahydrate (binders) | 3% |
| Sodium citrate (water softner) | 2% |
| Glycerol ether (Solvent) | 4% |
| Linear alkyl benzene sulphonate (30%) detergent | 27% |
| Sodium lauryl ether sulphate (28%) Detergent |
10% |
| Coconut diethanolamide (foam producer) | 3% |
| Water | 49% |
| Preservatives/ dyes | Q.S. |
Table 1: Traditional anionic car wash shampoo formulation [4].
Low Hydrophilic Lipophilic Balance (HLB) fatty alcohol ethoxylate/hydrotropic system replaced the traditional anionic surfactant-based car shampoo as they afford more effective cleaning performance; decreasing and they have low foam profile (Table 2)[5].
| Chemical compound | % By weight used the formulation |
|---|---|
| Fatty alcohol ethoxylate (low HLB) | 5% |
| Hydrophobe (alkyl glycoside or quaternary fatty amine ethoxylate) | 5%-10% |
| TKPP (Tetrapotassium Pyrophosphate) Detergent builder |
6% |
| Sodium metasilicate | 4% |
| Balance water |
Table 2: HLB fatty alcohol ethoxylate/hydrotropic car wash shampoo formulation [5].
Sodium citrate is known to be a water softener and a pH adjuster. It’s an ingredient in most common liquid detergents. It’s also used in some food products to adjust its acidity. It’s used in ice cream, gelatin desserts, candy and jelly. It’s also used in some pharmaceutical and personal care products, such as sunscreens, facial moisturizers, makeup, baby wipes, soaps, shampoos and conditioners [6].
Coconut di-ethanol amide is used as an emulsifying and foaming agent in personal care products and in cosmetics. It’s extracted from coconut oil. It’s also used in hydraulic fluids and industrial cooling lubricants [7].
Experiment
Linear alkyl benzene sulphonic acid with a chemical formula of CH3(CH2)11C6H4SO3H and a molecular mass of 326.49 is used as a mercerizing and washing agent in textile industry. It’s used as an emulsifier and wetting agent in small quantities with surfactants as it increases the surface area of distempers [8]. Because of its good performance and low cost linear alkylbenzene sulfonic acid is the largest volume synthetic anionic detergent. As all surfactants, linear alkylbenzene sulfonic acid has both hydrophilic and hydrophobic groups. Other examples of commercial anionic surfactants are alkyl sulfates and alpha-olefin sulfonates. These compounds are produced by sulfonation and they are non-volatile compounds. Linear alkylbenzene sulfonic acid consist of a phenyl isomer of 5 to 2 position substituents, different alkyl chain lengths consisting of ten to fourteen carbon atoms (C10-C14) and an aromatic ring sulfonated at the para position attached to the linear alkyl chain at any position except position 1, the 1-phenyl position. The chemical and physical properties of linear alkylbenzene sulfonic acid differ based on the length of the alkyl chain, giving rise to different formulations and different usage in various applications [9].
Sodium Lauryl Ether Sulphate (SLES) with a chemical formula of CH3 (CH2)11(OCH2CH2)nOSO3Na and a molecular mass of 421 g/ mol is used as a surfactant and it’s an anionic detergent. It’s a very effective foaming agent, inexpensive and used in shampoos, toothpastes and soaps [10].
Sodium Lauryl Sulphate (SLS) with a chemical formula of C12H25NaSO4 and a molecular mass of 288.4 g/mol is used in hygiene, cleaning, food and pharmaceutical products and it’s an anionic surfactant. It is widely used as food additives in the food industry and as emulsifier and an ionic solubilizer in the pharmaceutical industry [11].
Sodium Hydroxide Sulphate (SHS) with a chemical formula of NaOH and a molecular mass of 39.9 g/mol is a strong base, hygroscopic solid, soluble in water and can cause severe burns. It’s used in various industries; it’s used in the manufacture of drain cleaner, soaps, detergents, textiles, drinking water, pulp and paper. It’s used as paint stripper, cleaning agent, relaxer and in food preparation [12].
Betaine with a chemical formula of C5H11NO2 and a molecular mass of 117.146 g/mol is a chemical compound occurring in plants and it’s an amino acid; it’s a white solid at room temperature [13]. It is present in living cells and it’s a methylated nitrogen compound. It’s used in the pharmaceutical industry in the preparation of shampoo and soap as it’s a nonionic surfactant. Due to its high surface activity, its derivatives are used as efficient cleansing agents. It’s also used as viscosity modifiers, foam stabilizers and detoxifiers. Betaine esters can be used in antiperspirants as it processes anti-microbial activity [14].
Water with a chemical formula of H2O and a molecular mass of 18.01 g/mol is an inorganic compound that is odorless, tasteless, transparent liquid at room temperature, and act as solvent [15]. It’s present in 70% of the earth’s surface as seas and oceans [16]. In the world economy, 70% of water is used in agriculture [17].
Sodium triphosphate with a chemical formula of Na5P3O10 and a molecular mass of 367.864 g/mol is used as a component of industrial and domestic products in a large scale [18].
It’s used as a builder and a water softener in commercial detergents. Detergents are deactivated in water containing high concentrations of Mg2+ and Ca2+, hard water. It’s a chelating agent as it binds tightly to bications and prevents them from interfering with sulfonate detergent. It’s used as an emulsifier to retain moisture and it’s also used as a preservative in the food industry. It’s also used as anti-cracking agent, flame retardant, anti-corrosion pigment and as a synthetic tanning agent and masking agent in the leather industry [19].
Glycerol with a chemical formula of C3H8O3 and a molecular mass of 92.094 g/mol is an odorless and a non-toxic colorless viscous liquid at room temperature [20]. Glycerol is hygroscopic in nature and is miscible in water. It’s used as humectants in pharmaceutical formulations as it improves the ability of skin to absorb water and it’s used in the food industry as a sweetener [21].
Propylene Glycol (PG) with a chemical formula of C3H8O2 and a molecular mass of 76.095 g/mol is colorless viscous liquid at room temperature and has a faintly sweet taste. It’s miscible in a wide variety of solvents including chloroform, acetone and water. It’s a non-irritating substance with a low volatility [22]. It’s used in various industries including food and drug, anti-freezes, polymers and electronic cigarettes. It’s used as humectants in hand sanitizers to prevent skin drying [23]. It’s used in coffeebased drinks, ice creams, whipped dairy products, soda and liquid sweeteners [24]. Polypropylene glycol alginate gives rise to greater increase in form stability equal in the amount of neutral polysaccharides [25-27] (Table 3).
| Chemical name | Chemical structure | Molecular formula | Molecular weight (g/mol) | Amount used in the current formulation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear Alkyl Benzene Sulphonic Acid (LABSA) | 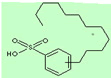 |
CH3(CH2)11C6H4SO3H | 326.49 | 5 |
| Sodium Lauryl Ether Sulphate (SLES) |  |
CH3(CH2)11(OCH2CH2)nOSO3Na | Variable; typically around 421 g/mol | 20 |
| Sodium Lauryl Sulphate (SLS) |  |
C12H25NaSO4 | 288.372 | 5 |
| Sodium Hydroxide |  |
NaOH | 39.997 | 1 |
| Betaine |  |
C5H11NO2 | 117.146 | 2 |
| Water (Dihydrogen Monoxide) |
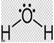 |
H2O | 18.01 | 61.5 |
| Sodium triphosphate |  |
Na5P3O10 | 367.864 | 3 |
Table 3: lists the Chemical name, molecular formula and molecular weight of chemical compounds used in the current formulation.
The current formulation consists of 1% builder in the form of sodium hydroxide, 3% water softener in the form of sodium triphosphate, 32% surfactants in forms of 5% Linear Alkyl Benzene Sulphonic Acid (LABS) , 20% Sodium Lauryl Ether Sulphate (SLES) and 5% Sodium Lauryl Sulphate (SLS) and 2.5% solvents in forms of 0.5% Propylene Glycol (PG) and 2% Glycerol.
Sodium and potassium hydroxides are known to be used in wheel rim cleaner formulation as the alloy wheel pick up dirt and grease from the road and they are prone to dirt from the abrasive wear of brake shoes [28,29]. The amount of sodium and potassium hydroxides used in the wheel rim cleaner formulation 0%-15% [3]. It isn’t known to be used in carwash formulations.
Other builders are known to be used in car wash formulations to soothe out slight imperfections and to remove road grease and stubborn tar from the bodywork of the vehicle. These builders would be calcium carbonate, silicones, and lamella aluminum silicates. To increase the quality of car wash shampoo formulation silicone derivative builders are added as to the formulation. Silicone derivative builders contribute to the ease of application of the products, the gloss and its water repellency property [2].
The amount of surfactant used in the current car wash shampoo formulation concentrate is 32% (5% Linear Alkyl Benzene Sulphonic Acid (LABS), 20% Sodium Lauryl Ether Sulphate (SLES), and 5% Sodium Lauryl Sulphate (SLS), and 2% Betaine). To increase the quality of the car wash shampoo, the amount of surfactants in the formulation must be increased to 37%.
solvents used in the current formulation: 0.5% propylene glycol and 2.0% glycerol, both are known to be used as humectants in pharmaceutical personal care product formulations to improve the ability of skin to absorb water. These solvents aren’t known to be used in car wash shampoo formulations. Other solvents used in car wash shampoo formulations (4% glycol ether) to aid in removal of surface dirt and to act as carrier for silicates and components of the shampoo. Solvents that are commonly are used in car wash shampoo formulations are glycol ethers such as di-propylene alcohol mono-methyl ether used as solvent to dissolve grease [2].
The choice of solvent is critical to avoid stress, cracking of plastics and to avoid damage to painted surface [2]. It isn’t recommended the use of glycerol or propylene glycol in the formulation and it’s recommended the use of glycol ether. Also, the amount of solvents used in the current formulation is low 2.5% compared to the amount used reference 4%. The amount of solvents used should be increased to 4% to increase the quality of the car wash shampoo formulation.
For the current formulation to dilute to a greater volume 500 L and to also maintain the quality of the car wash shampoo concentrate, the amount of surfactants, builders, foaming agents and solvents must be increased relative to the amount of the main solvent used to dissolve it’s components. The current formulation dilutes to 200 L, in order for the formulation to dilute to double this volume the amount of the main solvent used to dissolve its components must be decreased to ½ and the amount of surfactants/builders/foaming agents and solvents must be increased by 1½. Taking the traditional anionic car wash shampoo formulation as an example, the percentage of each chemical compound in the formulations would be: 3% sodium carbonate, 4.5% sodium metasilicate pentahydrate, 3% sodium citrate, 6% glycerol ether, 40.0% linear alkyl benzene sulphonate, 15% sodium lauryl ether sulphate, 4.5% coconut diethanolamide and 24.0% water as the dissolving solvent.
Conclusion
The current formulation for the contrite must be modified to increase its quality. It’s not recommended the use of sodium hydroxide as a builder or the use for glycerol/propylene glycol as solvents in the car wash shampoo formulation and the amount of surfactants must be increased to at least 37%.
The choice of builders and solvents are critical to avoid stresscracking of plastics and to avoid damage to painted surface.
Sodium hydroxide are known to be used in wheel rim cleaner formulation as the alloy wheel pick up dirt and grease from the road not in car wash shampoos, glycerol and propylene glycol are known to be used as humectants in lotions and personal care products. Sodium hydroxide, glycerol, and propylene glycol aren’t known to be used in car wash shampoo formulations.
Builders used in car wash shampoo formulations to remove road grease and stubborn tar from the bodywork of the vehicle, sooth out minor surface scratches and slight imperfections and contribute to the gloss, the water repellency, increase the durability of the overseas and to polish the paint work. Calcium carbonates, silicones, lamella aluminum silicates and poly dimethyl siloxane are known to be used in car wash shampoo formulations as builders.
To increase the quality of the car wash shampoo concentrate 2% sodium carbonate and 3% silicates should be used instead of 1% sodium hydroxide. It’s also recommended the use of a different solvent to dissolve grease and improve the quality of the car wash shampoo concentrate, 4% glycol ether.
Foaming and emulsifying agents are missing from the current formulation, 3% coconut diethanolamide. Coconut diethanolamide are used to dissolve solvents, builders, silicates and facilitate the formation of foams.
For a liter of concentrate dilute to 500 L, the amount of builders, solvents and surfactants must be increased to 1½ and the amount of water must be decreased to ½.
Acknowledgement
I would like to sincerely thank the association of consulting chemist and chemical engineers for their efforts in making our profiles available for clients in the USA and worldwide.
References
- www. sakagroup.com
- Company M, Karsa DR (2007) Handbook for Cleaning/ Decontamination of Surfaces, Amsterdam, the Netherlands, Elsevier B.V.
- Hauthal H.G, Wagner G (2004) Household Cleaning, Care and Maintenance Products: Chemistry, Application, Ecology and Consumer Safety, pub1. Verlag Fur chemischeIndustrie H Ziolkowsky GmbH.
- Surfactants Selector; A Guide to the Selection of I&I and Household Product Formulations, Akcros Chemicals (1998) (now part of Akzo Nobel Surface Chemistry AB).
- Akzo Nobel Surface Chemistry AB, S 444 85 Stenungsund, Sweden.
- www. sakagroup.com
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sodium_laureth_sulfate
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sodium_dodecyl_sulfate
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sodium_hydroxide
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trimethylglycine
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Water
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sodium_triphosphate
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glycerol
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Propylene_glycol
- World of Chemicals, 2022, Linear Alkylbenzene Sulfonic Acid.
- Valappil K,Lalitha S, Gottumukkala D, Sukumaran RK,Pandey A (2015) White biotechnology in cosmetics, industrial biorefineries& white biotechnologypp 607-652.
[Crossref], [Google Scholar], [Indexed]
- "Water Q&A: Why is water the "universal solvent"?".
- "CIA–THE WORLD FACTBOOK Geography Geographic overview". Central Intelligence Agency
- Baroni L, Cenci L, Tettamanti M, Berati M (2007) Evaluating the environmental impact of various dietary patterns combined with different food production systems". Eur J ClinNutr 61: 279-286.
[Crossref], [Google Scholar], [Indexed]
- Complexing agents, Environmental and Health Assessment of Substances in Household Detergents and Cosmetic Detergent Products, Danish Environmental Protection Agency, Accessed 2008-07-15.
- Schrodter K, Bettermann G, Staffel T, Wahl F, Klein T et al., (2008) "Phosphoric Acid and Phosphates". Ullmann'sencycl ind chem 19: 145.
[Crossref], [Google Scholar]
- Oxford Dictionaries–English, glycerol-Definition of glycerol in English by Oxford Dictionaries".
- Christoph R, Schmidt B, Steinberner U, Dilla W, Karinen R (2006) "Glycerol" Ullmann'sencycl ind chem 12: 144.
[Crossref], [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan, Carl J, Kuenz A, Vorlop, Klaus D (2018) "Propanediols" Ullmann'sencycl ind chem 12: 163.
[Crossref], [Google Scholar]
- Lohrey, Jackie. "Ingredients in Hand Sanitizer".
- "Quackmail: Why You Shouldn't Fall For The Internet's Newest Fool, The Food Babe". Butterworth, Trevor. Forbes.
- Jackson G, Roberts RT, Wainwright T (1980) "Mechanism of Beer Foam Stabilization by Propylene Glycol Alginate" J Inst Brew 86: 34–37.
[Crossref], [Google Scholar]
- PersianUTab, “Sodium citrate in detergents”.
- Contact Dermatitis Institute, “Coconut diethanolamide”.
Open Access Journals
- Aquaculture & Veterinary Science
- Chemistry & Chemical Sciences
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Health Care & Nursing
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Materials Science
- Mathematics & Physics
- Medical Sciences
- Neurology & Psychiatry
- Oncology & Cancer Science
- Pharmaceutical Sciences